本文介绍 C++ 中的类型转换。
部分内容来自C++元编程和C++右值。隐式转换部分和重载决议有关,需要结合起来看。
涉及 type 的一些概念
Incomplete type
- void 以及其 cv-qualified 形式
- incompletely-defined object type
一个 class 被声明(比如一个前向声明),却没有定义。
bound 未知的数组。
imcomplete type 构成的数组。
enum,从它的声明,到它的 underlying type 被确定期间。
这里说明一下,bound 未知的数组未必是 flex 数组。它可能是如下面这种 extern 形式定义的
1 | extern int x[]; // the type of x is "array of unknown bound of int" |
Incomplete type 经常让人头大,需要各种头文件魔法或者 pimpl 来解决。
在下列情况下,需要类型是 Complete 的:
- TODO
typd-id
我们可以通过 class/union/enum/typedef/using(type alias) 这些方式定义一个具名的类型。但是在 C++ 中,我们经常使用那些不具名的类型,例如下面的情况。
1 | int* p; // declaration of a pointer to int |
此外,RTTI 机制还提供了一个 typeid 运算符(不是函数)
1 | int main() { |
显式类型转换
显式转换有几种类型:
(new-type) expr 型。这是 C-style 的,C++ 会按顺序尝试:
- const_cast
- static_cast(增强的)
注意,子类的指针或者引用,可以被转成无歧义的基类,即使基类不可访问。对于成员函数的指针也同样适用 - static_cast(增强的) + const_cast
- reinterpret_cast
- reinterpret_cast + const_cast
new-type (expr) 型。
需要注意,这种 function-style cast expression 容易和声明产生歧义。此时,这些歧义都会被视作声明。
1 | struct M {}; |
【C++11起】new-type {expr}型。
一个显式类型转换的类型是什么呢?
- 对于 lvalue reference,结果是一个 lvalue
- 对于函数的 rvalue reference,结果是一个 lvalue
- 对于 rvalue reference,结果是一个 xvalue
- 对于其他情况,结果是一个 prvalue
Value categories
- 一个 glvalue,即 generalized lvalue 是一个表达式,对它求值 determines the identity of an object or function。
- 一个 prvalue 即 pure rvalue,是一表达式,对它求值
- 计算某个 builtin 操作符的操作数
这种情况称作这个 prvalue 没有 result object。 - 初始化某个对象
这种情况称作这个 prvalue 有 result object。
结果对象可以是一个变量,或者由 new 表达式创建的对象,或者由临时量实质化创建的临时对象,或者前述三类对象的成员。
注意非 void 的弃值表达式有 result object,称为 materialized temporary。
并且除了作为 decltype 的操作数,每个类类型或数组类型的纯右值都有 result object。
- 计算某个 builtin 操作符的操作数
- 一个 xvalue,即 eXpiring value 是一个 glvalue,它的资源能够被重新利用
- an lvalue 是一个 glvalue,但不是 xvalue。
- an rvalue 是一个 prvalue 或者 xvalue。
一些定义
temporary materialization
提一个temporary materialization 的概念。指的是一个完整类型 T 的 prvalue,可以被转换成同类型 T 的一个 xvalue。
下面是天书,看不懂。
This conversion initializes a temporary object of type T from the prvalue by evaluating the prvalue with the temporary object as its result object, and produces an xvalue denoting the temporary object. If T is a class or array of class type, it must have an accessible and non-deleted destructor.
根据下面的例子来看,应该是 S() 是个 prvalue,然后通过 evaluating S() 得到了一个 temporary object 作为 result object,然后创建了一个 xvalue 去表示这个 temporary object。
1 | struct S { int m; }; |
Temporary materialization occurs in the following situations:
- when binding a reference to a prvalue;
- when performing a member access on a class prvalue;
- when performing an array-to-pointer conversion (see above) or subscripting on an array prvalue;
- when initializing an object of type
std::initializer_list<T>from a braced-init-list; - when typeid is applied to a prvalue (this is part of an unevaluated expression);
- when sizeof is applied to a prvalue (this is part of an unevaluated expression);
- when a prvalue appears as a discarded-value expression.
Move-eligible expressions
Although an expression consisting of the name of any variable is an lvalue expression, such expression may be move-eligible if it appears as the operand of
- a return statement
- a co_return statement (since C++20)
- a throw expression (since C++17)
If an expression is move-eligible, it is treated:
- either as an rvalue or as an lvalue(until C++23)
- as an rvalue(since C++23)
…for the purpose of overload resolution (thus it may select the move constructor).
但这里还有个特例,就是 Guaranteed copy elision
If expression is a prvalue, the result object is initialized directly by that expression. This does not involve a copy or move constructor when the types match (see copy elision).
我理解这里的 Move-eligible expressions 就是像下面这个语句,是可以 implicit move 的。在其他情况下,都应该显式 std::move()。后面在支持协程的时候,可能标准委员会发现要加点补丁这样子了。
1 | A func(A a) { |
lvalue
- 解引用
- ++a 等
- +=、=、%= 等
a.m和a.*mpp->m和p->*mp- 逗号运算符
a ? b : c的一些情况
可以参考 https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/operator_other#Conditional_operator,但这里非常复杂。- 字符串直接量
- 返回左值的 cast
xvalue
a.m和a.*mp
其中 a 是一个 rvalue,m 是 a 的一个非静态成员。
这里区分同种类型中是左值的情况。a, b
其中 b 是 xvalue。a ? b : c
可以参考 https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/operator_other#Conditional_operator,但这里非常复杂。- 一个函数调用,或者一个 operator,它返回的是 rvalue,例如
std::move(x) a[n]
对数组取下标。我理解就不包含 operator[],这不废话么,operator[] 按照上一条不也是一样的么- any expression that designates a temporary object, after temporary materialization
- 一个 Move-eligible expression
In particular, like all rvalues, xvalues bind to rvalue references, and like all glvalues, xvalues may be polymorphic, and non-class xvalues may be cv-qualified.
prvalue
- literal
- 一个函数调用或者 overloaded operator expression,它的返回值如果不是引用
- 某些 builtin operator
a++ 等,注意 ++a 是 lvalue。 - 某些三目运算符的计算结果
- this
- enumerator
- lambda 表达式
User-defined conversion function
用户自定义的类型转换函数,用来支持显式或者隐式地从某个 class 类型转化到另一个类型。
有三种方式:
- operator conversion-type-id
- 【C++11】 explicit operator conversion-type-id
只允许在 direct-initialization 和 explicit conversions 场景下使用。 - 【C++20】 explicit ( expression ) operator conversion-type-id
需要注意,conversion-type-id 中不能带有 [] 或者 ()。如果想提供到某个数组指针或者函数的转换,我们需要先 typedef 一下。但无论如何,任何情况下都不能转化成数组或者函数。
1 | struct X |
下面的代码展示了 implicit 和 explicit 的 conversion 的区别。
1 | struct X |
对于隐式转换而言,user-defined conversion function 发生在第二阶段,在本文的对应章节有论述。
隐式类型转换
一个隐式类型转换序列包含:
一系列 standard conversion sequence
可选的 user-defined conversion
一个 user-defined conversion 包含两种情况:- 由0或1个单参数的Converting constructor
这里指的是没有被标记为 explicit 的构造函数。 - 一个 non-explicit conversion function call
这里指的是1
operator conversion-type-id
- 由0或1个单参数的Converting constructor
一系列 standard conversion sequence
When considering the argument to a constructor or to a user-defined conversion function, only a standard conversion sequence is allowed (otherwise user-defined conversions could be effectively chained). 当一个 non-class 类型转换到另一个 non-class 类型,只允许一个 standard conversion sequence。
Standard conversion 的顺序:
- zero or one conversion from the following set: lvalue-to-rvalue conversion, array-to-pointer conversion, and function-to-pointer conversion;
- zero or one numeric promotion or numeric conversion;
- 【C++17】 zero or one function pointer conversion;
- zero or one qualification conversion.
当且仅当 T2 能从 表达式 e 被 copy-initialized 时,也就是说 T2 t = e 是 well-formed 时,e 可以被隐式转换为 T2。这里注意 copy-initialized 不是 direct initialization T2 t(e)。对于后者,需要考虑 explicit constructors 和 conversion functions。
Converting constructor
简单再介绍下 Converting constructor。总的来说,构造函数分为两类,explicit constructor 和 converting constructor。explicit constructor 只在 direct initialization,其中包含显式类型转换比如 static_cast 时使用。converting constructor 在 copy initialization 也可以被使用,此时作为 user-defined conversion sequence,其实就是上面讲的第二阶段的一部分。
1 | struct A |
对于上面的定义,下面列出了一些 case。
1 | int main() |
一个有趣的问题
为什么 optional::value_or 接受一个 U&& 参数而不直接使用 T&&呢?
原因有两个:
U&&实际上是一个 universal reference,方便我们进行完美转发- 构造默认的值的成本可能比较大,例如他可能是有100个元素的一个 vector。如果实际不需要用到这个默认的值,使用 U&& 能允许我们做一个优化,让它不被构造。方案是引入一个 U,这个 U 只是一个 generator,只有在实际被用到也就是调用
operator T()时,才会生成一个 vector。如果在调用 value_or 之前就将 U&& 转换为 T&&,这个优化就不能做了。
当然了,我还是觉得 rust 的方案好,也就是让你传一个 closure 过去。
decay
首先来看一下什么是 decay。例如,对于数组 T a[n],除了 sizeof、alignof、引用限定符 & 以及字符串常量等少数情形外,a出现时会被 decay 成指向 T 的指针。例如下面代码往 char s[N] 数组中读入了数据
1 | scanf("%s", s); |
而很多人会误写为以下的代码
1 | scanf("%s", &s); |
此时,s 的类型实际上是 char (*) [N],称为 pointer to an array of char ,而 scanf 希望接受到的是char *,称为 pointer to char 类型。
各种 convertion 类型
Contextual conversions
Case1: 【C++11】从 T 到 bool 的转换。如果 bool t(e) 是 well-formed,也就是说存在 explicit T::operator bool() const;。在下列场景中,这样的表达式 e 会被转换为 bool:
- if、while、for 的条件
- 逻辑运算符
- 三目运算符的条件
- static_assert
- noexcept
- 【C++20】explicit 表达式
Case2: In the following contexts, a context-specific type T is expected, and the expression e of class type E is only allowed if:
- 【until C++14】E has a single non-explicit (since C++11) user-defined conversion function to an allowable type.
- 【since C++14】对于 E 的所有的 non-explicit conversion functions,如果它们的返回类型是都是 T,或者带 CV 和引用修饰的 T,这样的 e 可以 implicitly convertible to T。
Such expression e is said to be contextually implicitly converted to the specified type T. 【C++11】Note that explicit conversion functions are not considered, even though they are considered in contextual conversions to bool.
- the argument of the delete-expression (T is any object pointer type);
- integral constant expression, where a literal class is used (T is any integral or unscoped (since C++11) enumeration type, the selected user-defined conversion function must be constexpr);
- the controlling expression of the switch statement (T is any integral or enumeration type).
Value transformations
Lvalue-to-rvalue conversion
不考虑旧版本,从 C++11 开始说。
一个非 function 且非 array 类型的 glvalue T 可以被隐式转换为一个 prvalue。此时:
- 如果 T 不是 class type, 那么这个 prvalue 的类型是 T,但会去掉 cv 限定符。
- 如果 T 是 class type,那么这个 prvalue 的类型是 T。
如果 T 是一个不完整类型,那么执行 lvalue-to-rvalue conversion 是 ill-formed 的。
When an lvalue-to-rvalue conversion is applied to an expression E, the value contained in the referenced object is not accessed if:
- E is not potentially evaluated,也就是它是 unevaluated operand,或者 unevaluated operand 中的子表达式。
- the evaluation of E results in the evaluation of a member Ex of the set of potential results of E, and Ex names a variable x that is not odr-used by Ex.
Array-to-pointer conversion
An lvalue or rvalue of type “array of N T” or “array of unknown bound of T” can be implicitly converted to a prvalue of type “pointer to T”.
【C++17】If the array is a prvalue, temporary materialization occurs.
The resulting pointer refers to the first element of the array (see array to pointer decay for details)
Function-to-pointer conversion
Numeric promotions
Integral promotion
Floating-point promotion
Numeric conversions
Integral conversions
Floating-point conversions
Floating–integral conversions
Pointer conversions
Pointer-to-member conversions
Boolean conversions
Qualification conversions
【C++17】Function pointer conversions
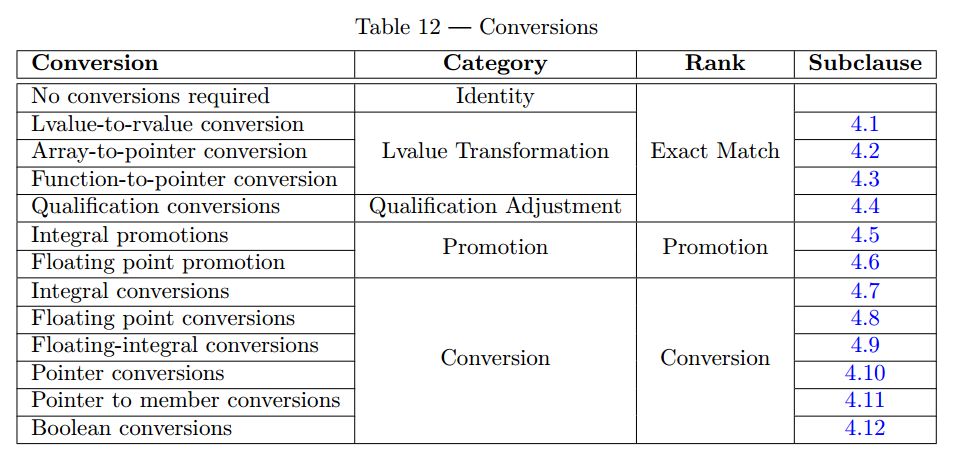
重载决议的顺序(rank)
在重载决议时,采取下列顺序,可参考 Ranking of implicit conversion sequences 章节。
任何一个 standard conversion sequence 被划分为下面三个 rank:
精确匹配
此时,不需要进行任何的转换。
下面列举出了几种情况:- 无转换
- Lvalue-to-rvalue conversion
- 【C++17】function pointer conversion
- user-defined conversion of class type to the same class
- Qualification conversions,即限定符转换
我们可以为任意类型加上CV限定符。对于多重指针来说,前面的重数的限制要高于后面重数的限制,如1
2
3char** p = 0;
const char** p1 = p; // error: level 2 more cv-qualified but level 1 is not const
const char* const * p2 = p; // OK: level 2 more cv-qualified and const added at level 1
Promotion
即Numeric promotions,包含Integral promotion和Floating-point promotion
这里注意,非promotion的整数之间转换都作为conversion,如char -> intConversion
- integral conversion
- floating-point conversion
- floating-integral conversion
- pointer conversion
- pointer-to-member conversion
- boolean conversion
- user-defined conversion of a derived class to its base
The rank of the standard conversion sequence is the worst of the ranks of the standard conversions it holds (there may be up to three conversions)
注意能进行隐式类型转换并不意味着类型相同,所以使用std::is_same进行的判断都是false,例如下面的代码输出都是false。
1 | std::cout << std::is_same<int, int &>::value << '\n'; |

